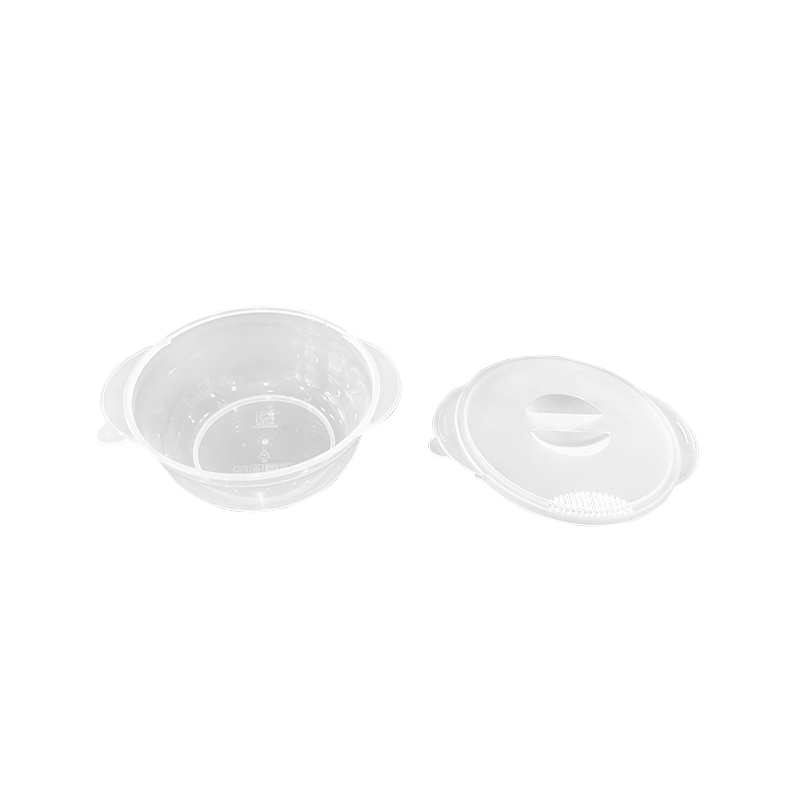
The Plastic Thin Space Cup Mould represents an innovation in the manufacturing o...
-
+86-15068654601
-

No.62 Zhao Feng Road, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang, China
+86-15068654601

No.62 Zhao Feng Road, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang, China
Material selection is a key issue for thin wall space cups because the product requires both light weight and sufficient mechanical strength. Common materials include high-performance thermoplastics such as polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), and polycarbonate (PC). These materials offer good flow properties, allowing them to fill thin-wall cavities effectively.

However, thin wall moulding demands materials with stable melt flow and consistent viscosity. Inconsistent material batches or moisture content can bring about defects such as flow marks, short shots, or surface waviness. Additionally, the material must withstand processing temperatures without degrading, as thin wall parts often require high injection speed and pressure.
Therefore, material quality control, including drying, moisture testing, and consistent supply from certified manufacturers, is critical to achieving stable production.
Thin wall space cup moulding is technically demanding due to the thin cavity design and high-speed injection requirements. Common challenges include warpage, sink marks, and incomplete filling.
Warpage and Dimensional Instability
Thin wall parts cool rapidly, uneven shrinkage. This can cause deformation and dimensional inaccuracy if cooling channels and mold temperature control are not properly designed.
Short Shot and Flow Marks
Insufficient injection speed or pressure can result in incomplete filling. Flow marks appear when the melt front cools too quickly, leaving visible lines on the surface.
High Stress and Part Fragility
Thin wall parts are more prone to stress concentration. Improper gate design or excessive packing pressure may bring about internal stress and cracking.
To address these issues, manufacturers often use advanced simulation tools, optimize gate location, and employ high-performance injection moulding machines capable of precise control.
Cost and cycle time are closely linked in thin wall space cup manufacturing. Thin wall moulding typically requires high injection speed, high pressure, and precise temperature control. As a result, the moulding machine must be capable of fast response and stable performance.
Cycle time is generally shorter for thin wall parts because the thin section cools quickly. While shorter cycle time can improve productivity, it also increases demands on the machine's clamping system and cooling efficiency. The mould itself must be designed to handle rapid cycles without overheating or wearing prematurely.
The moulding process also requires high-quality tooling and precise machining, which increases upfront investment. However, long-term production can be cost-effective due to material savings and high throughput. The balance between initial tooling cost and long-term production efficiency is a common concern for manufacturers.
Quality consistency is a key focus area for thin wall space cup production. Small variations in process parameters can significantly affect part quality. To ensure consistent results, manufacturers typically implement strict process control and monitoring.
Process Parameter Monitoring
Monitoring injection pressure, melt temperature, cooling temperature, and cycle time helps maintain stable production. Automated systems can detect deviations and trigger adjustments.
Mould Maintenance and Inspection
Regular inspection of mould cavities, cooling channels, and gate systems prevents defects caused by wear or blockage. Maintenance schedules help maintain consistent surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Quality Inspection Methods
Common inspection methods include dimensional measurement, visual inspection, and material testing. For high-precision parts, coordinate measuring machines (CMM) and non-destructive testing may be used.
Through these measures, manufacturers can achieve reliable production performance and consistent product quality.