The Plastic Thin Space Cup Mould represents an innovation in the manufacturing o...
-
+86-15068654601
-

No.62 Zhao Feng Road, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang, China
+86-15068654601

No.62 Zhao Feng Road, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang, China
Thin wall space cups used to produce these cups directly affects product quality, production efficiency, material usage, and long-term manufacturing cost. When asking which thin wall space cup mould is the best choice, there is no single universal answer. The best choice depends on production scale, material type, machine configuration, quality requirements, and budget constraints.
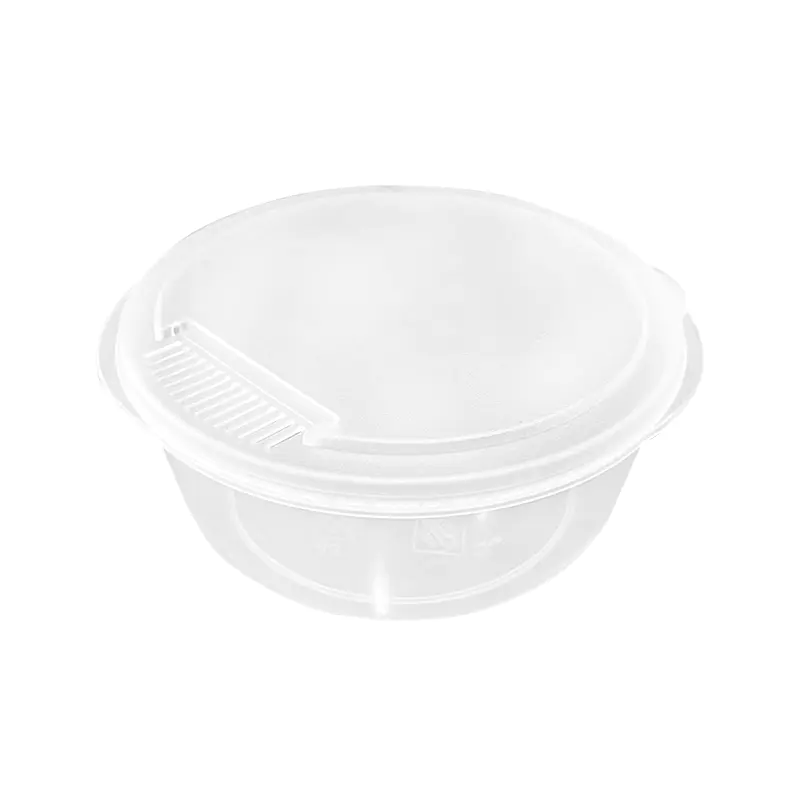

Single-Cavity vs. Multi-Cavity Moulds
One of the first decisions in selecting a thin wall space cup mould is whether to use a single-cavity or multi-cavity layout. Single-cavity moulds are more suitable for product testing, small-batch production, and new product development. They allow easier adjustment of processing parameters and simpler maintenance. However, their production output is limited.
Multi-cavity moulds, which may contain 4, 8, 16, or even more cavities, are designed for mass production. They significantly increase hourly output and reduce unit production cost. For manufacturers with stable large orders, multi-cavity moulds are usually the more practical option. The trade-off is higher initial mould cost and stricter requirements for balance in filling, cooling, and ejection across all cavities. If the runner system or cooling channels are not well balanced, differences in wall thickness and weight between cups may occur.
Therefore, the best choice between single and multi-cavity moulds depends primarily on expected production volume and investment planning.
Cold Runner vs. Hot Runner System
Runner system selection plays a central role in thin wall cup mould performance. Cold runner moulds are structurally simpler and have lower manufacturing costs. Melt flows through solid runners that are ejected along with the product. While suitable for some general injection products, cold runners generate significant material waste and increase cycle time due to runner cooling and separation.
Hot runner systems, in contrast, keep the plastic melt in a heated state up to the gate. This eliminates runner waste and improves material utilization. For thin wall space cups, hot runner moulds are often preferred because they enable fast filling at stable temperatures, which is essential for preventing short shots and uneven thickness. They also support higher automation levels since no runner separation is required.
However, hot runner systems involve higher initial cost and require careful temperature control and maintenance. The best choice depends on whether long-term production volume justifies the investment and whether the manufacturing team has sufficient technical capability to manage hot runner systems.
Mould Steel and Surface Treatment
Mould steel selection directly influences service life, surface finish of the cups, and maintenance frequency. For thin wall space cup moulds, commonly used steels include P20, H13, S136, and similar pre-hardened or hardened tool steels. These materials provide a balance between machinability, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.
Because thin wall cups are usually used for food or beverage applications, surface requirements are strict. Smooth cavity surfaces are needed to ensure clean demoulding and uniform cup appearance. Polishing quality affects both transparency and ease of release. In addition, corrosion resistance becomes important when producing with certain resins or when frequent washing and cleaning are required.
Some moulds also use surface coatings or nitriding treatments to improve hardness and wear resistance. The best steel choice is therefore not simply the hardest or most expensive option, but the one that matches expected production volume, resin type, and maintenance conditions.
Cooling System Design and Cycle Efficiency
Efficient cooling is one of the most critical factors in thin wall space cup moulds. Because the wall thickness is small, the melt cools quickly, but uneven cooling can easily cause warpage, ovality, or inconsistent cup height. High-quality moulds use precisely arranged cooling channels that follow the contour of the cavity and core as closely as possible.
In some designs, beryllium copper inserts are used in high-heat concentration areas to improve thermal conductivity. Uniform cooling across all cavities is especially important in multi-cavity moulds to ensure consistent product weight and stacking performance.
The best mould choice is one that offers balanced cooling efficiency rather than simply the shortest nominal cycle time. Inconsistent cooling may lead to higher rejection rates, which ultimately reduces effective productivity.
Ejection System and Product Stability
Thin wall cups are lightweight and sensitive to deformation. The ejection system must release the product smoothly without causing distortion, scratches, or rim damage. Common ejection methods include stripper rings, air ejection, and sleeve-type ejection systems.
Stripper rings are frequently used for thin wall cups because they provide uniform force around the cup circumference. Air ejection assists in reducing vacuum adhesion between the core and the product. A well-designed ejection system contributes to stable automatic production and minimizes downtime caused by stuck parts.
The best mould is one that combines mechanical ejection with air assistance in a coordinated way to ensure reliable demoulding at high speed.