The Plastic Thin Space Cup Mould represents an innovation in the manufacturing o...
-
+86-15068654601
-

No.62 Zhao Feng Road, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang, China
+86-15068654601

No.62 Zhao Feng Road, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang, China
Plastic chairs are widely used in homes, offices, schools, and public spaces due to their lightweight, durability, and ease of maintenance. In China, the production of plastic chairs is a major industry, supported by advanced injection moulding technology. The mould used for producing these chairs plays a crucial role in determining the quality, efficiency, and cost of manufacturing. Understanding the common classifications of China plastic chair moulds helps manufacturers, designers, and buyers make informed decisions.
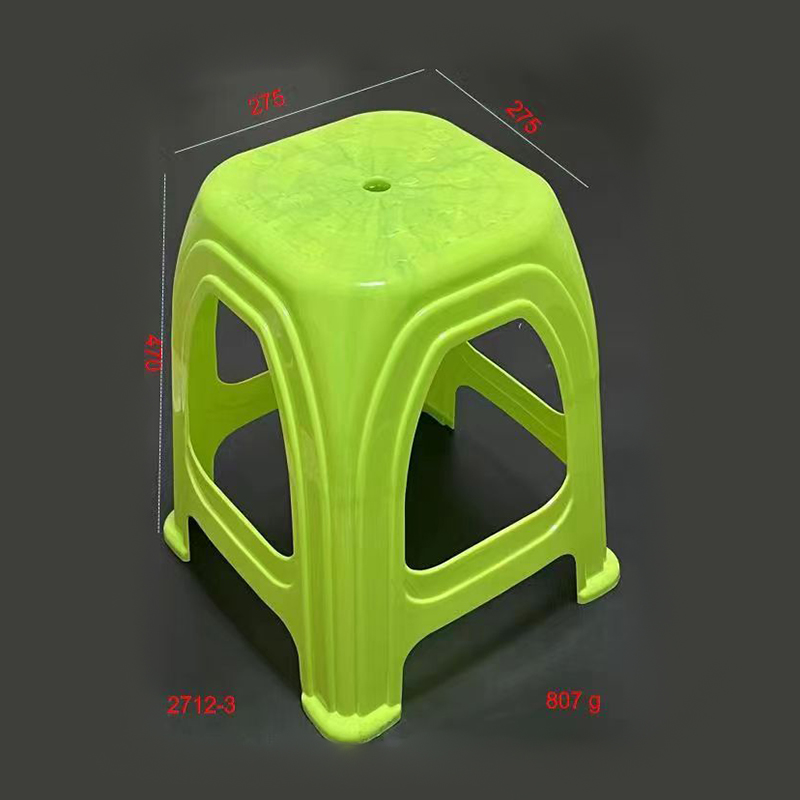

1. Classification by Structural Type
(1) Single-cavity moulds
Single-cavity moulds produce one chair per injection cycle. These moulds are generally used for smaller production volumes or for specialized designs. For example, a furniture workshop producing customized chairs for boutique hotels may use a single-cavity mould to maintain control over design precision and surface finish. Single-cavity moulds are simpler and less costly to manufacture, but their production rate is lower compared to multi-cavity alternatives.
(2) Multi-cavity moulds
Multi-cavity moulds allow the production of multiple chairs per cycle. These are often employed in large-scale manufacturing facilities to increase output while maintaining consistent quality. In a factory producing school chairs for mass distribution, a multi-cavity mould might produce four or six identical chairs simultaneously, improving efficiency and reducing production time. Multi-cavity designs require more precise control of injection pressure and cooling systems to ensure uniformity across all cavities.
(3) Stack moulds
Stack moulds feature multiple layers of cavities, effectively doubling or tripling output without significantly increasing the mould footprint. Factories producing chairs for large-scale events or public venues sometimes use stack moulds to meet high demand within limited factory space. The stack mould design allows simultaneous injection in different layers, reducing cycle time while optimizing floor space utilization.
2. Classification by Material Type
(1) Polypropylene (PP) moulds
PP is the common plastic used for chair production due to its durability, lightweight nature, and ease of colouring. Moulds designed for PP require attention to shrinkage rates and proper venting to ensure smooth surfaces. Many household plastic chairs in China, often sold through retail chains or online platforms, are produced using PP-specific moulds.
(2) Polycarbonate (PC) moulds
PC moulds are designed for transparent or semi-transparent chairs. These materials are more rigid and resistant to impact than PP, which requires higher precision in mould temperature control and cooling. An example is the production of modern office chairs with a transparent backrest, where PC moulds help achieve both aesthetic clarity and structural strength.
(3) Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) moulds
ABS is used for chairs that require a higher level of rigidity and surface finish. ABS moulds must be designed to accommodate the material’s higher processing temperatures and shrinkage characteristics. For instance, premium cafeteria chairs in Chinese universities often use ABS moulds to ensure durability and a smooth, polished appearance.
3. Classification by Production Capacity
(1) Prototype and low-volume moulds
These moulds are intended for trial runs, design verification, and limited production batches. Furniture designers in China often use prototype moulds to test ergonomics, aesthetics, and structural integrity before moving to full-scale production. Prototype moulds allow rapid iteration and design adjustments without committing to expensive large-scale moulds.
(2) Medium-volume production moulds
Moulds designed for medium-volume production are commonly used by small to medium-sized factories. They balance production speed with cost efficiency. For example, manufacturers producing chairs for residential use in local markets may rely on this type of mould to meet consistent demand without over-investing in high-capacity tooling.
(3) High-volume production moulds
High-volume moulds are used in large factories producing chairs for mass markets, including schools, restaurants, and public institutions. These moulds are typically multi-cavity or stack designs to maximize output while maintaining uniformity. A practical example is a Chinese factory supplying millions of plastic chairs annually to nationwide educational institutions.
4. Classification by Technological Features
(1) Standard injection moulds
These moulds employ conventional injection technology suitable for general-purpose chair production. They are widely used in factories producing chairs with simple designs and standard dimensions.
(2) Gas-assisted injection moulds
This technology involves injecting gas into the molten plastic to reduce material usage, weight, and cycle time. Factories producing lightweight yet strong chairs for outdoor use often use gas-assisted moulds. For instance, a manufacturer producing garden chairs may adopt this technique to reduce raw material consumption while retaining structural integrity.
(3) Hot-runner moulds
Hot-runner systems maintain plastic in a molten state within the runners, reducing waste and improving surface finish. High-end furniture producers use hot-runner moulds for chairs that require intricate patterns, consistent colours, and minimal post-processing.