The Plastic Thin Space Cup Mould represents an innovation in the manufacturing o...
-
+86-15068654601
-

No.62 Zhao Feng Road, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang, China
+86-15068654601

No.62 Zhao Feng Road, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang, China
At its core, a plastic injection molding machine is a device used to manufacture plastic products by injecting molten plastic material into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape. This process, known as injection molding, is one of the widely used methods for producing plastic components, especially when large volumes and consistent quality are required.
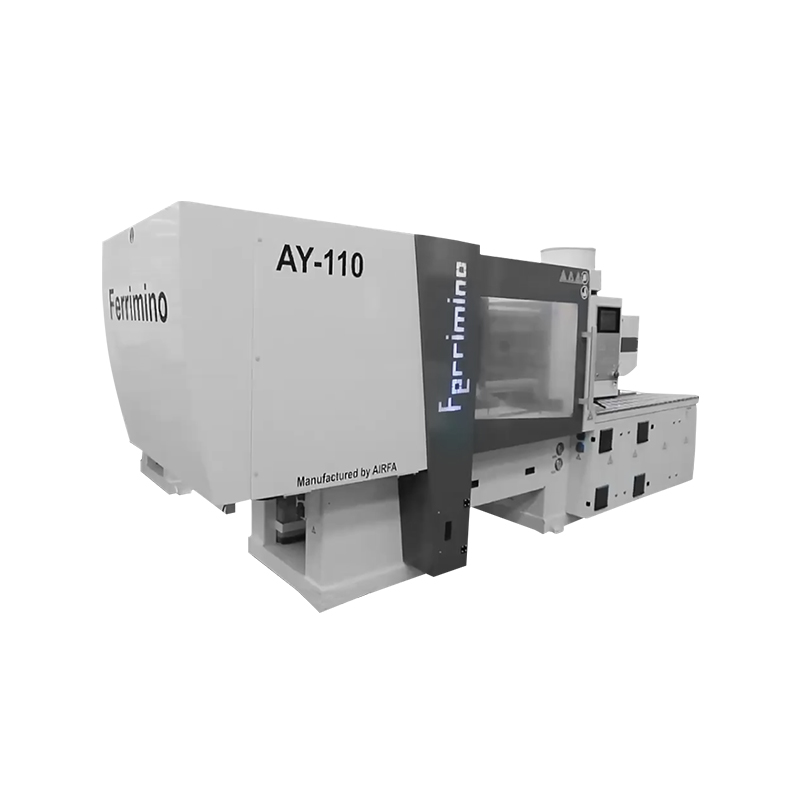

The machine essentially combines heating, melting, and precise injection of plastic material, followed by cooling and ejection of the finished part. This integrated approach allows manufacturers to produce complex shapes with tight tolerances, smooth finishes, and repeatable results.
The injection molding process involves several key steps, all facilitated by the machine's components:
Material Feeding and Melting: Plastic raw material, usually in pellet form, is fed into a heated barrel by a hopper. Inside the barrel, a rotating screw or plunger heats and melts the plastic to a molten state.
Injection: The machine's screw or plunger pushes the molten plastic through a nozzle and injects it into a mold cavity under high pressure. The mold is a precisely machined tool that shapes the plastic.
Cooling: Once the cavity is filled, the plastic cools and solidifies inside the mold, taking the exact form of the cavity.
Ejection: After solidification, the mold opens, and ejector pins push the finished part out of the mold, ready for collection.
Cycle Repeat: The mold closes again, and the cycle repeats continuously.
The entire process is highly automated and controlled by the machine's control system, allowing precise adjustment of temperature, pressure, injection speed, and cooling time.
Main Components of Plastic Injection Molding Machines
A typical plastic injection molding machine consists of several essential components:
Injection Unit: This includes the hopper, barrel, screw or plunger, and nozzle responsible for melting and injecting the plastic material.
Clamping Unit: It holds the mold in place and applies force to keep it closed during injection and cooling. This unit then opens the mold to eject the part.
Control System: Modern machines feature computerized control panels for managing process parameters and ensuring consistent operation.
Mold: Though technically separate, the mold is an integral part of the system, shaping the injected plastic.
Types of Plastic Injection Molding Machines
Plastic injection molding machines come in various types, classified mainly by their driving mechanisms and specific applications:
Hydraulic Injection Molding Machines: These use hydraulic cylinders for injection and clamping. They are traditionally common and capable of generating high force but tend to be less energy efficient.
Electric Injection Molding Machines: Powered by electric servo motors, these machines offer precise control, faster cycle times, and energy efficiency. They are increasingly favored in industries requiring high precision and clean operation.
Hybrid Injection Molding Machines: Combining hydraulic and electric systems, hybrids balance energy efficiency with high clamping force and speed.
Vertical Injection Molding Machines: With a vertical clamping mechanism, these are used for insert molding and specific applications where vertical mold opening is advantageous.
Applications of Plastic Injection Molding Machines
Plastic injection molding machines serve a broad range of industries, producing parts for:
Automotive: Components like dashboards, bumpers, and interior trims.
Consumer Goods: Household items, containers, toys, and electronics casings.
Medical Devices: Syringes, diagnostic components, and surgical instruments.
Packaging: Caps, closures, and containers.
Industrial Parts: Gears, valves, and machine housings.
Their versatility and ability to produce complex geometries make injection molding machines essential in modern manufacturing.