The Plastic Thin Space Cup Mould represents an innovation in the manufacturing o...
-
+86-15068654601
-

No.62 Zhao Feng Road, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang, China
+86-15068654601

No.62 Zhao Feng Road, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang, China
Plastic furniture storage boxes have become a staple in homes, offices, and warehouses, offering practical solutions for organizing and storing various items. These boxes are lightweight, durable, and versatile, making them ideal for both personal and industrial use. The manufacturing of these storage boxes relies heavily on injection moulding, a process that involves shaping molten plastic material within a pre-designed mould to create the desired shape. A plastic furniture storage box injection mould plays a pivotal role in ensuring that these products are of high quality, consistent in shape, and durable over time.
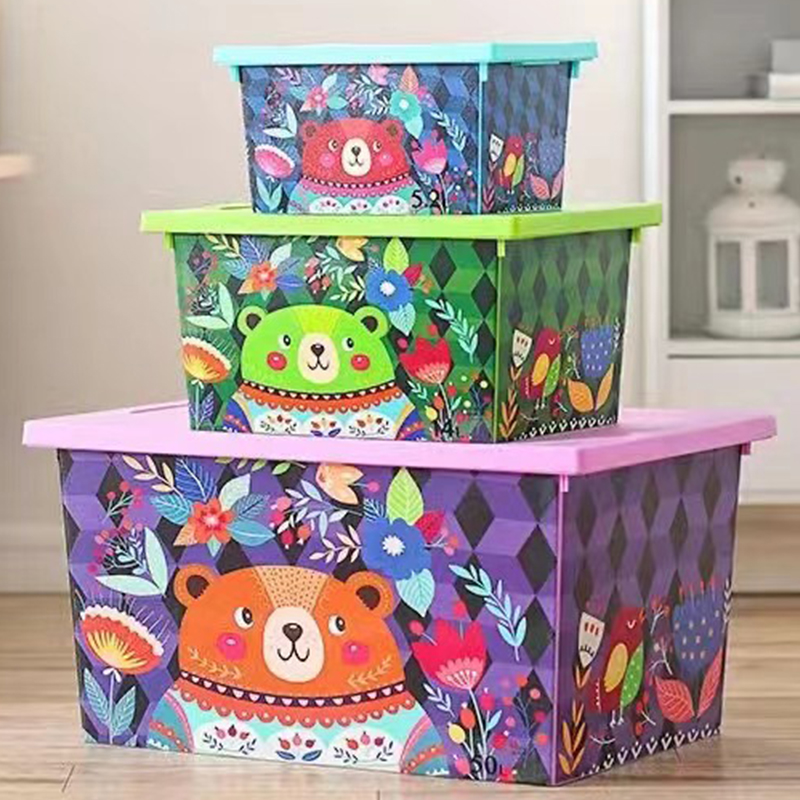

Injection moulding is a widely used manufacturing process that involves injecting molten plastic material into a mould cavity under high pressure. The plastic material is then allowed to cool and solidify, taking the shape of the mould. This process is used to produce a variety of plastic products, including furniture storage boxes, containers, and other household items.
The injection mould itself is a metal tool designed to create the specific shape of the plastic product. The mould for a plastic furniture storage box must be precisely engineered to ensure that the final product meets the required specifications for size, strength, and functionality. The mould consists of two halves: the cavity (which holds the shape of the storage box) and the core (which forms the inside of the box).
The design of the injection mould is critical to ensuring that the plastic storage box is manufactured accurately and efficiently. Several factors must be considered when designing a mould for furniture storage boxes:
a) Mould Material Selection
The material used for the mould itself is essential for the durability and performance of the moulding process. Common materials for moulds include steel and aluminium. Steel is often preferred for its strength and ability to withstand high-pressure injection moulding, making it ideal for mass production. Aluminium, on the other hand, is more cost-effective and easier to machine, making it suitable for shorter production runs or when less durability is required.
b) Mould Design Features
The design features of the mould will directly affect the quality and ease of production. These features include:
Ventilation: Proper venting is crucial to avoid air traps and ensure smooth flow of molten plastic into the mould cavity. Without adequate venting, defects such as bubbles or incomplete filling can occur.
Cooling Channels: The cooling system in the mould ensures that the plastic solidifies at the right temperature. Efficient cooling channels help reduce cycle times and improve production efficiency.
Ejection Mechanism: Once the plastic has cooled and solidified, the mould must be able to release the storage box without causing damage. An efficient ejection system, such as pins or plates, is needed to push the finished product out of the mould.
Draft Angles: Draft angles are slight slopes added to the walls of the mould to help release the part easily from the mould cavity. These angles ensure that the furniture storage box can be ejected without causing deformation.
c) Mould Cavities
The number of cavities in the mould determines the number of parts produced in one cycle. A single-cavity mould produces one item per cycle, while multi-cavity moulds produce multiple items at once, enhancing production efficiency. The choice between single and multi-cavity moulds depends on the volume of production required and the complexity of the storage box design.